Obtain right Cross-Correlation spectrum
Contents
1 Background
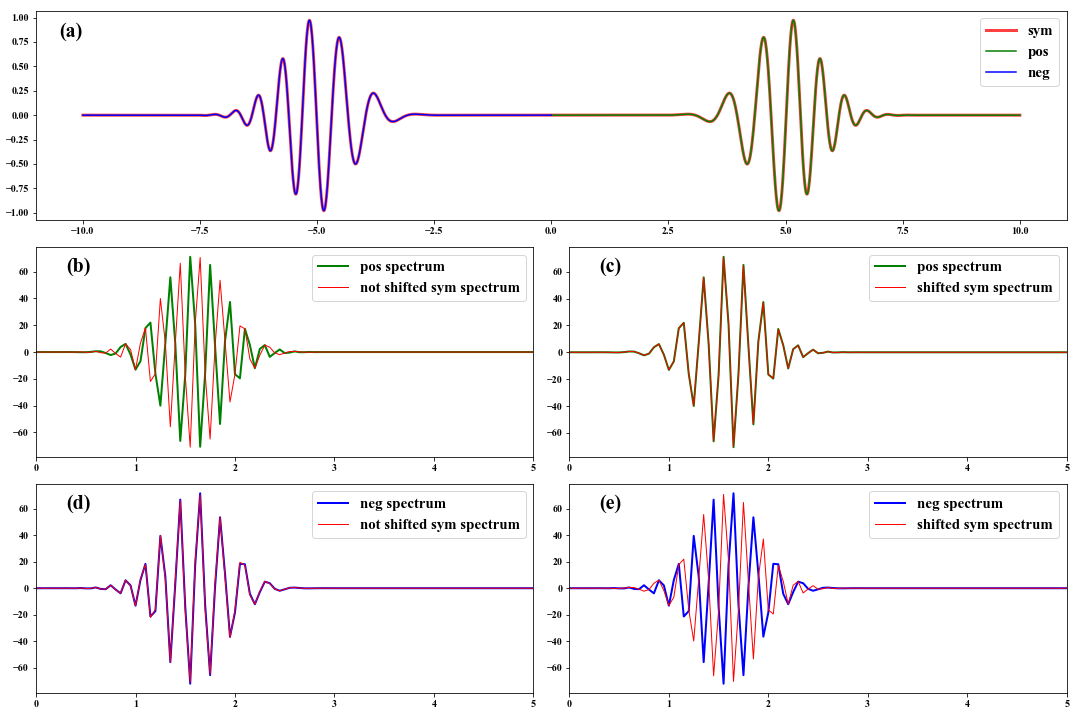
Ambient seismic noise cross-correlation has far-reaching implications for the passive seismic surface wave imaging from regional to continental scales (e.g. Campillo & Paul, Shapiro & Campillo, 2004). Spectral analysis of cross-correlations is the key to retrieving reliable dispersion information about surface waves. Based on the Fourier spectra of event seismic surface wave data, however, we need to shift the cross-correlation time function before doing FFT to obtain the right spectra.
2 A numerical example
Here, we generate a linear frequency modulated signal with decaying as $e^{-(t-t0)^2}$, and create a symmetric signal like cross-correlation functions extracted from seismic noise. The Fourier spectra separately from shifted and not shifted symmetric signal will be compared with the spectra of the positive and negative signals.
|
|
Bibliography
Campillo, M., & Paul, A. (2003). Long-range correlations in the diffuse seismic coda. Science, 299(5606), 547–549.
Shapiro, N. M., & Campillo, M. (2004). Emergence of broadband rayleigh waves from correlations of the ambient seismic noise. Geophysical Research Letters, 31(7).
Author Geophydog
LastMod 2020-12-28
